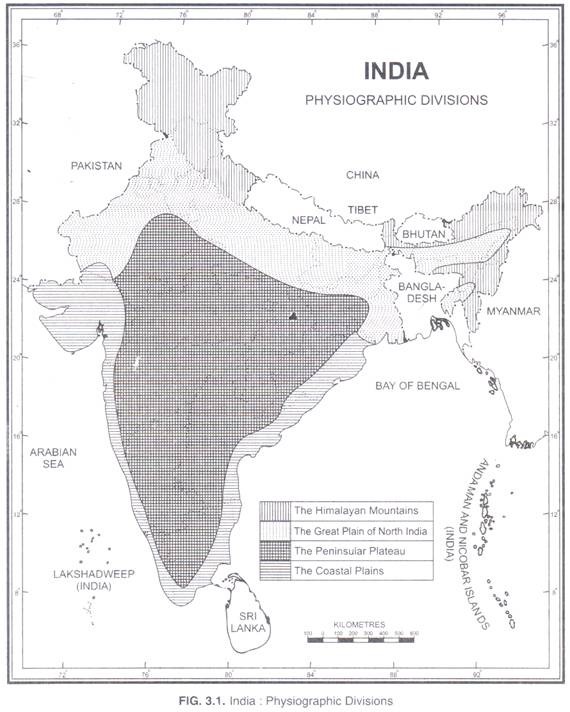
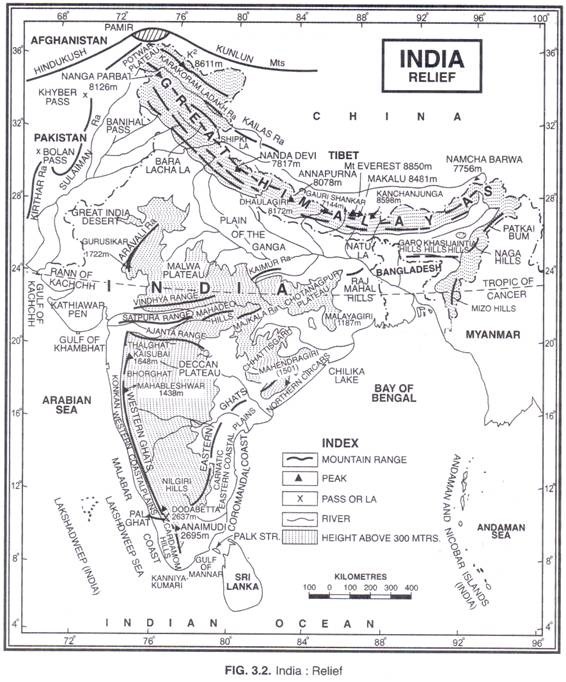
Here is your Short Paragraph on the Himalayan Mountains !
The Himalayan Mountains are also known as the Himadri, Himavan or Himachal. The Himalayas consist of the youngest and the loftiest mountain chains in the world.
The magnitude of their size can be estimated from the fact that the central axial range of the main Himalayas alone stretches for a distance of over 2,400 km (over 22° longitude) from the Indus gorge in the west to the Brahmaputra gorge in the east.
The width of the Himalayas varies from 500 km in Kashmir to 200 km in Arunachal Pradesh. The total area of the Himalayan mountain region is nearly five lakh sq km. The Pamir, popularly known as the roof of the world is the connecting link between the Himalayas and the high ranges of Central Asia.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
From the Pamir, the Himalayas extend eastward in the form of an arcuate curve which is convex to the south. The southern boundary of the Himalayas is well defined by the foothills (300 m contour line) but the northern boundary is rather obscure and merges with the edge of the Tibet Plateau.
The Himalayas have attained a unique personality owing to their high altitude, steep gradient, snow capped summits, deeply dissected topography, youthful drainage, complex geological structure and rich temperate flora in the subtropical latitudes.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The Himalayan mountain chains have the lofties peaks of the world. The number of peaks higher than 8,000 metre is 14 and those over 7,500 metre total 20. Of the 94 Asian peaks which exceed 7,300 metre, all but two are in the Himalaya and Karakoram ranges. The number of peaks over 7,000 metre runs into hundreds and several peaks above 6000 metre have not been adequately counted and mapped. Many of them have not been even given their names till now.